문제
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr

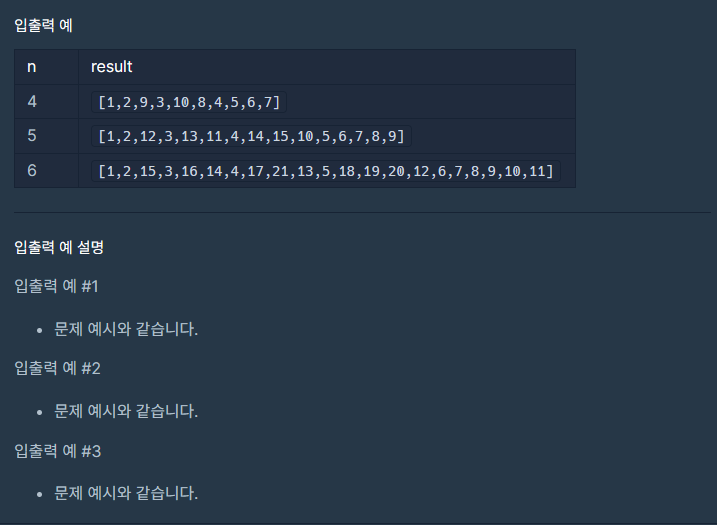
1 번째 시도
두 가지 생각이 떠올랐다.
1. 배열 자리 순서대로 숫자의 규칙을 찾아보자
2. 숫자가 증가하는 순서대로 자료구조에 집어넣자
처음엔 규칙을 발견하는 것이 알고리즘 짜기 쉽기 때문에 1번 방법을 선택했다.
n = 7 과 n =8을 만들어보면서 규칙을 찾아봤는데 쉽지 않아. 결국 2번을 택했다.
로직을 설명 하자면 숫자가 증가하는 것과 마찬가지로 큰 데두리 삼각형에 숫자를 집어넣고 작은 테두리 삼각형에 숫자를 집어넣는 방식이다.
↙
↙ ↖
↙ ↙ ↖ 꼭대기에서 부터 시작하여 요런 방식으로 숫자를 집어넣는 것이다.
↙ ↙ ↖ ↖
↙ ↙ ↙ ↖ ↖
↙ ↙ → → ↖ ↖
↙ → → → → → ↖
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int n) {
ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
int lastNumber = 0;
for(int i= 1; i <= n; i++ ) {
lastNumber += i;
}//마지막 숫자 초기화
for(int i =1; i <= n; i++) {
int[] array = new int[i];
list.add(array);
} //배열에 계단식 자료구조 초기화
int top = 0; // 현재 삼각형 맨 꼭대기 층을 가르킨다
int bottom = n-1; //현재 삼각형 맨 아래층을 가르킨다
int left =0; //현재 삼각형 맨 왼쪽 인덱스
int right = 0; // 현재 삼각형을 탐색할 때 가르키는 층 맨 오른쪽 인덱스
int present = 1; // 현재 숫자
while(present != lastNumber) { // 테두리 삼각형 돌기 반복
for(int i= top; i <= bottom; i++ ) {
list.get(i)[left] = present++;
right++;
}
right--; //루프가 끝나면 인덱스 +1 오바해서 가르키기 때문에
for(int j = left+1; j < right-1; j++) {
list.get(bottom)[j] = present++;
}
for(int k = bottom; k > top; k--) {
list.get(k)[right] = present++;
right--;
}
right+=2; //루프가 끝나면 현 층보다 -1 가르키기 때문에 현층의 다음층을 가르킨다
top += 2; // 다음 테두리 삼각형으로 넘어갈 때 top 다시 초기화
bottom--; // 다음 테두리 삼각형으로 넘어갈 때 높이 줄이기
left++; // 다음 테두리 삼각형으로 넘어갈 때 삼각형 밑변 줄이기
}
int[] result = new int[lastNumber];
int z = 0;
for(int x =0; x < n; x++) {
for(int y =0; y <x+1; y++) {
result[z] = list.get(x)[y];
z++;
}
} //이차원 List -> 일차원 배열로 변경
return result;
}
}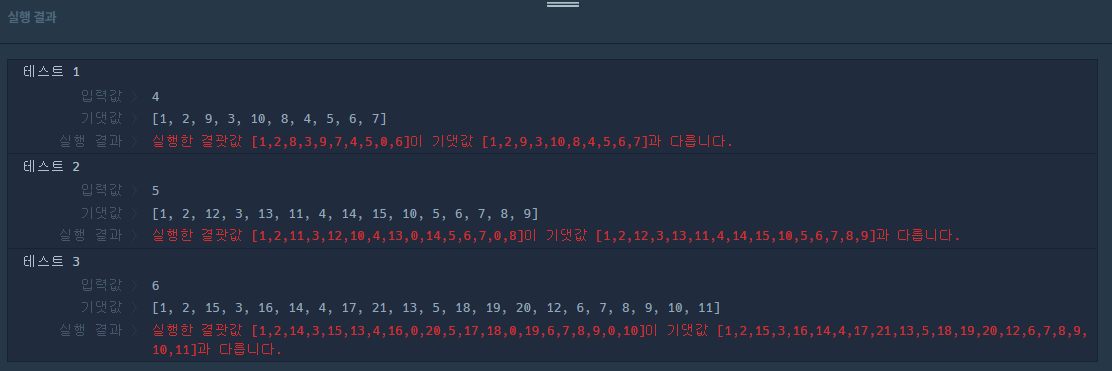
테투리 삼각형 맨 아랫줄에서 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 채우는 로직이 잘못된 것 같다. while 안에 있는 for문 3개를 수정해보겠다.
2 번째 시도
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int n) {
ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
int lastNumber = 0;
for(int i= 1; i <= n; i++ ) {
lastNumber += i;
}//마지막 숫자 초기화
for(int i =1; i <= n; i++) {
int[] array = new int[i];
list.add(array);
} //배열에 계단식 자료구조 초기화
int top = 0; // 현재 삼각형 맨 꼭대기 층을 가르킨다
int bottom = n-1; //현재 삼각형 맨 아래층을 가르킨다
int left =0; //현재 삼각형 맨 왼쪽 인덱스
int right = 0; // 현재 삼각형을 탐색할 때 가르키는 층 맨 오른쪽 인덱스
int present = 1; // 현재 숫자
while(present <= lastNumber) { // 테두리 삼각형 돌기 반복
for(int i= top; i <= bottom; i++ ) {
list.get(i)[left] = present++;
if(i != bottom)
right++;
}
for(int j = left+1; j < right; j++) {
list.get(bottom)[j] = present++;
}
for(int k = bottom; k > top; k--) {
list.get(k)[right] = present++;
if(k != top+1)
right--;
}
top += 2; //루프가 끝나면 현 층보다 -1 가르키기 때문에 현층의 다음층을 가르킨다
bottom--; // 다음 테두리 삼각형으로 넘어갈 때 높이 줄이기
left++; // 다음 테두리 삼각형으로 넘어갈 때 삼각형 밑변 줄이기
}
int[] result = new int[lastNumber];
int z = 0;
for(int x =0; x < n; x++) {
for(int y =0; y <x+1; y++) {
result[z] = list.get(x)[y];
z++;
}
} //이차원 List -> 일차원 배열로 변경
return result;
}
}
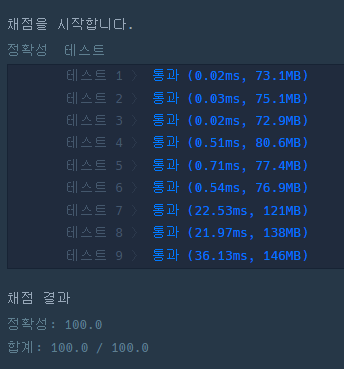
성공! 통과는 했지만, 오늘도 역시나 다른 사람의 코드를 보며 부족한 점을 채워보겠다.
다른 사람 코드
다른 분은 x,y,direction 변수로 삼각형을 탐색했다.
변수가 줄어드니 유지보수는 더 쉬울 것 같다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int n) {
ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
int lastNumber = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
lastNumber += i;
} // Calculate last number
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int[] array = new int[i + 1];
list.add(array);
} // Initialize arrays in list
int number = 1; // Start filling with 1
int x = 0; // Start at top-left of the triangle
int y = 0;
int direction = 0; // 0: down, 1: right, 2: up
while (number <= lastNumber) {
list.get(x)[y] = number++; // Fill number
// Determine next position based on direction
if (direction == 0) { // Moving down
if (x + 1 < n && list.get(x + 1)[y] == 0) {
x++;
} else {
direction = 1;
y++;
}
} else if (direction == 1) { // Moving right
if (y + 1 < list.get(x).length && list.get(x)[y + 1] == 0) {
y++;
} else {
direction = 2;
x--;
y--;
}
} else if (direction == 2) { // Moving up
if (x - 1 >= 0 && list.get(x - 1)[y - 1] == 0) {
x--;
y--;
} else {
direction = 0;
x++;
}
}
}
// Convert to single array
int[] result = new int[lastNumber];
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list.get(i).length; j++) {
result[idx++] = list.get(i)[j];
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] result = solution.solution(4); // Example usage
for (int num : result) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
배운 점
- 사실 내 코드가 금방 나온 것 같지만 오류를 잡아내지 못해 3시간 동안 혼자 생각했다.
top,bottom,left,right 신경써야 할 것이 많아 시뮬레이션 돌려보기 힘들었다.
다음 번에 더 유지보수하기 쉬운 코드로 짜야겠다. - 미들 문제만 풀다 챌린저 문제를 풀었는데 구현하기 쉽지 않았다. 오랜 시간이 걸렸지만 아이디어를
코드로 구현할 수 있는 능력이 한 단계 성장한 것 같아 뿌듯하다.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 항해99 TIL 8일차 (피보나치 수 / 프로그래머스) (0) | 2024.04.02 |
|---|---|
| 항해99 TIL 7일차 (크기가 작은 부분 문자열 / 프로그래머스) (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| 항해99 TIL 5일차 (숫자 문자열과 영단어 / 프로그래머스) (0) | 2024.03.30 |
| 항해99 TIL 4일차 (체육복 / 프로그래머스) (1) | 2024.03.29 |
| 항하99 TIL 3일차(바탕화면 정리/프로그래머스) (0) | 2024.03.28 |



