#문제
레벨: G3
알고리즘: 구현 + bfs 조금
풀이시간: 2시간
힌트 참조 유무: 유
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/20058

#문제 풀이
이 문제는 bfs문제로 분류되어있지만, 사실상 구현문제라 생각한다. 이 문제에 핵심은 격자회전시키는 식을 잘 세울 수 있는지이다.
그 방법을 바로 말하겠다. 오른쪽으로 90도 회전한다고 하면 map[i][j]가 map [j][n-1-i]가 된다. 즉, i와 j를 바꿔주고 열은 n-1에다가 바꾼 i를 빼준다. (왼쪽으로 90도 회전한다고 하면 거꾸로 돼서 map[i][j]가 map[n-1-j][i]가 된다.) 우리는 덩어리 째 회전을 시켜야 하므로 이중 for문에서 i+=L 씩 증가시켜줘야 한다.
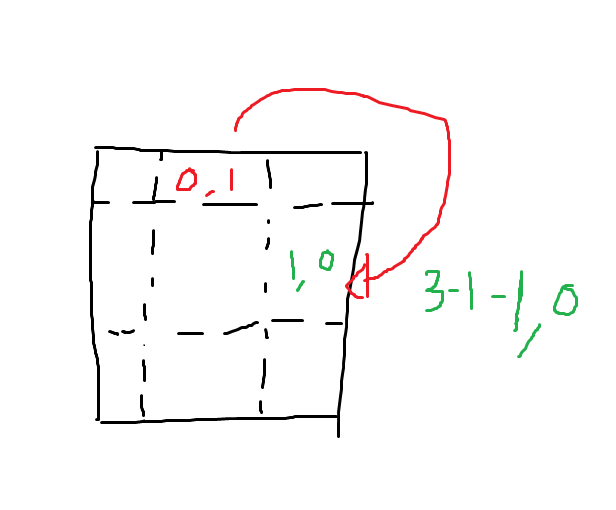
위 방식을 이해하고 구현은 다르게 되어있다. 내가 설명한 바로는 빨간색 글씨가 어디로 갈지로 설명한 거고 구현은 초록색 글씨 자리에 무엇이 와서 채워지는가로 구현되어있다.(그러니 왼쪽 90도 회전으로 구현되어있다.)
//분할 후 돌리기
public static int[][] divide(int L) {
int[][] tmp = new int[n][n];
L = (int) Math.pow(2, L);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += L) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += L) {
rotate(i, j, L, tmp);
}
}
return tmp;
}
// 돌리기
public static void rotate(int x, int y, int L, int[][] tmp) {
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < L; j++) {
tmp[x + i][y + j] = map[x + L - 1 - j][y + i];
}
}
}
#풀이 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int n, q;
public static int[][] map;
public static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
public static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static int land, totalIce;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
q = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
n = (int) Math.pow(2, n);
map = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int[] L = new int[q];
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
L[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
// 파이어스톰 시전
map = divide(L[i]);// 회전
map = melt();// 얼음 녹이기
}
land = totalIce = 0;
biggest();
System.out.println(totalIce);
System.out.println(land);
}
public static int[][] divide(int L) {
int[][] tmp = new int[n][n];
L = (int) Math.pow(2, L);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += L) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += L) {
rotate(i, j, L, tmp);
}
}
return tmp;
}
public static void rotate(int x, int y, int L, int[][] tmp) {
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < L; j++) {
tmp[x + i][y + j] = map[x + L - 1 - j][y + i];
}
}
}
public static int[][] melt() {
int[][] tmp = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tmp[i] = Arrays.copyOf(map[i], n);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int cnt = 0;
if (map[i][j] == 0)
continue;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (map[nx][ny] > 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
if (cnt < 3)
tmp[i][j]--;
}
}
return tmp;
}
public static void biggest() {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
totalIce += map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] > 0 && !visit[i][j]) {
q.add(new int[] { i, j });
visit[i][j] = true;
int cnt = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = q.poll();
int tx = t[0];
int ty = t[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = tx + dx[k];
int ny = ty + dy[k];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (map[nx][ny] > 0 && !visit[nx][ny]) {
visit[nx][ny] = true;
q.add(new int[] { nx, ny });
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
land = Math.max(land, cnt);
}
}
}
}
}
//출처; https://velog.io/@kimmjieun/%EB%B0%B1%EC%A4%80-20058%EB%B2%88-%EB%A7%88%EB%B2%95%EC%82%AC-%EC%83%81%EC%96%B4%EC%99%80-%ED%8C%8C%EC%9D%B4%EC%96%B4%EC%8A%A4%ED%86%B0-Java-%EC%9E%90%EB%B0%94'알고리즘 > 구현' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 2504] 괄호의 값 / 자바 / 구현(괄호) (0) | 2024.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [백준 17144] 미세먼지 안녕! / 자바 / 구현 (0) | 2024.08.02 |
| [백준 13458] 시험감독 / 자바 /그리드 (0) | 2024.07.03 |
| [백준 3190] 뱀 / 자바 / 구현 (0) | 2024.07.03 |
| 항해 21일차 99 TIL (공원산책/프로그래머스) (0) | 2024.04.18 |



