문제
레벨: G4
알고리즘: DFS
풀이시간: 1시간
힌트 참조 유무: 유
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1967
1 번째 시도: 실패
[깨달은 점]
dfs는 리턴값이 void이고 전역변수를 고치는 게 구현하기 편함 리턴값이 int면 구현하기 까다로움
[알고리즘 설명]
지름의 중심점이 될 수 있는 노드는 자식을 2개 가지고 있는 노드이다.
그래서 중심점이 될 수 있는 노드들을 dfs하며 답을 업데이트해간다.
dfs는 루트노드에서 양갈래로 찢어져 가장 각각 가장 긴 길을 구한다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
static int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
static int N;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> list;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
String[] s1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
int parent = Integer.parseInt(s1[0]);
int child = Integer.parseInt(s1[1]);
int value = Integer.parseInt(s1[2]);
list.get(parent).add(new Node(child, value));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (list.get(i).size() >= 2) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(new Node(i, 0), 0, 0));
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
public static int dfs(Node childNode, int cnt, int depth) {
int child = childNode.child;
int value = childNode.value;
cnt += value;
int res = cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < list.get(child).size(); i++) {
if (depth == 0) {
cnt += dfs(list.get(child).get(i), res, depth + 1);
} else {
cnt = Math.max(cnt, dfs(list.get(child).get(i), res, depth + 1));
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static class Node {
int child;
int value;
public Node(int child, int value) {
this.child = child;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
입력값
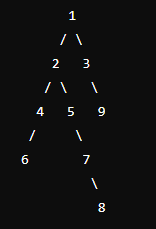
9
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 4 4
2 5 1
4 6 5
5 7 6
7 8 7
3 9 8같은 입력값을 넣었는데 어쩔 때(입력값 복붙하고 8를 삭제한 후 다시 8입력 후 엔터) 는 108이 나오고 어쩔 때(복붙 후 바로 엔터)는 27이 나온다.
[예측 실패 이유: 미제]
dfs 함수가 현재 노드에서 자식 노드로 내려갈 때마다 cnt 값을 누적하는 방식 때문에 이 문제가 발생한 것 같다. 근데 그렇다 하더라도 매번 출력값이 같아야 하는 거 아닌가?
2 번째 시도 : 성공
dfs 리턴 값을 void로 수정했다.
아무 노드나 하나 dfs로 탐색하여 가장 먼 노드를 찾고
'찾은 가장 먼 노드'에서 또 한 번 dfs를 탐색하면 '전에 찾은 가장 먼 노드'와 '가장 먼 노드'를 찾을 수 있다. 그럼 이 두 노드 사이의 간격이 가장 긴 간격이다
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
static int N;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> list;
static int maxDist;
static int farthestNode;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
String[] s1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
int parent = Integer.parseInt(s1[0]);
int child = Integer.parseInt(s1[1]);
int value = Integer.parseInt(s1[2]);
list.get(parent).add(new Node(child, value));
list.get(child).add(new Node(parent, value));
}
maxDist = -1;
dfs(1, -1, 0);
maxDist = -1;
dfs(farthestNode, -1, 0);
System.out.println(maxDist);
}
public static void dfs(int currentNode, int parentNode, int currentDist) {
if (currentDist > maxDist) {
maxDist = currentDist;
farthestNode = currentNode;
}
for (Node neighbor : list.get(currentNode)) {
if (neighbor.child != parentNode) {
dfs(neighbor.child, currentNode, currentDist + neighbor.value);
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int child;
int value;
public Node(int child, int value) {
this.child = child;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
'알고리즘 > DFS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 1707] 이분 그래프 / 자바 / dfs (0) | 2024.07.13 |
|---|---|
| [백준 14500] 테트로미노 / 자바 / DFS + 구현 (1) | 2024.07.03 |
| [백준 1987] 알파벳 / 자바 / 백트래킹 (0) | 2024.06.19 |
| [백준 1167] 트리의 지름 / 자바 / 트리순회(dfs) (0) | 2024.05.06 |
| [백준 10026] 적록색약 / 자바 / 그래프 순회(dfs) (0) | 2024.05.05 |



